Hydrogen and
Fuel Cell Technology
Hydrogen can be produced using renewable energy sources such as wind or solar power by using electrolyzers. These are essentially reverse fuel cells, and produce hydrogen by splitting water into oxygen and hydrogen. Hydrogen is used as an energy carrier and presents a viable energy storage solution, particularly for balancing the renewable energy grid.
When burned, hydrogen produces only heat and water, hence the name hydrogen: “water-former” in Greek. In our fuel cell systems, we convert the hydrogen into water in a more controlled manner, producing electricity instead of flames. Still, the only byproduct of the reaction is water.
PEM Fuel Cell Systems
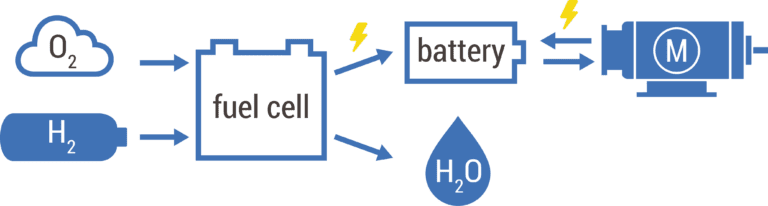
When used in our fuel cell systems, hydrogen is combined with oxygen (gathered from the ambient air surrounding the system) to transform the chemical energy stored in the fuel (hydrogen) and oxidizer (oxygen) into electrical energy and water vapour. The electrical energy gained from this electrochemical reaction can be used to power every application.
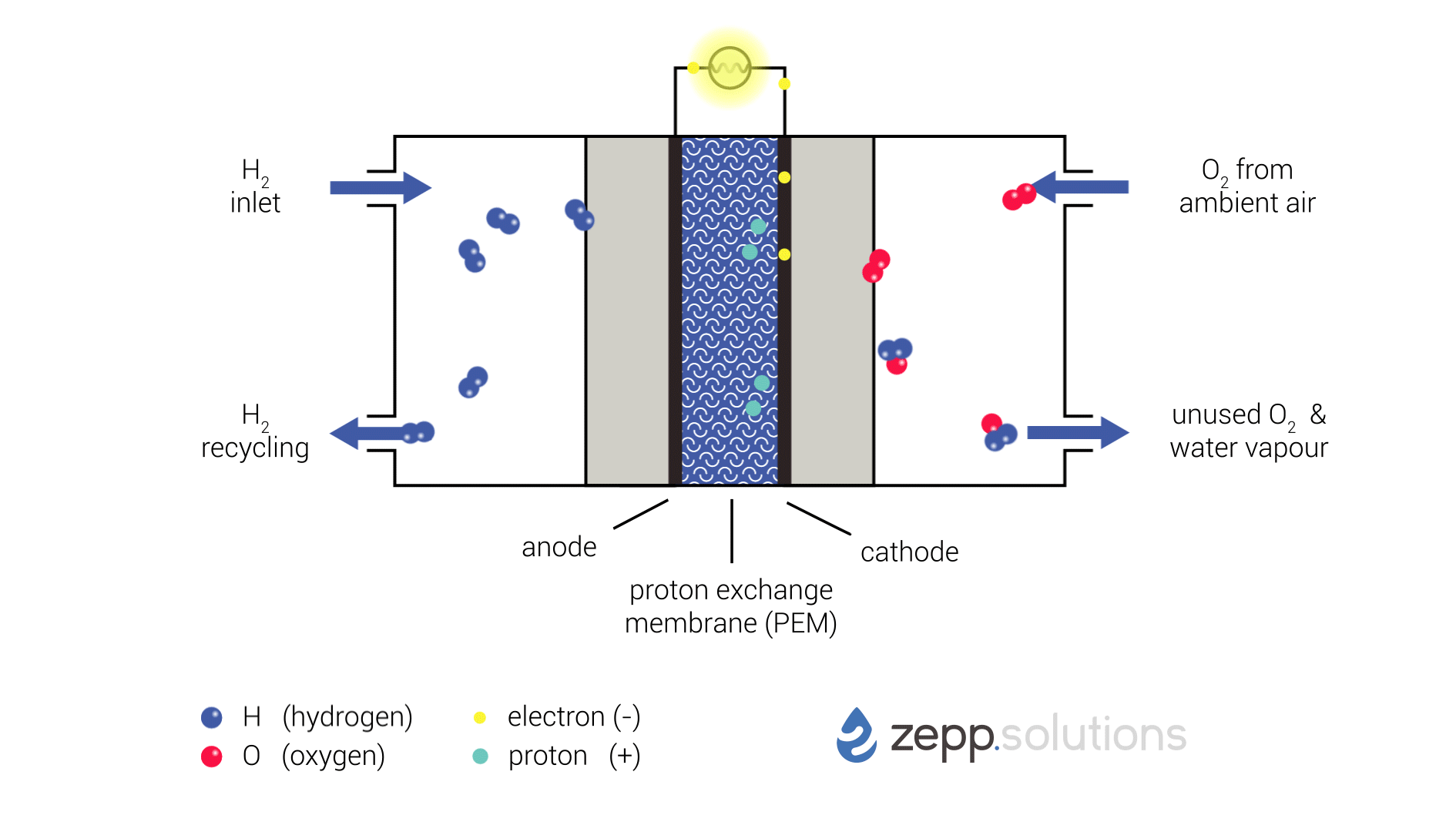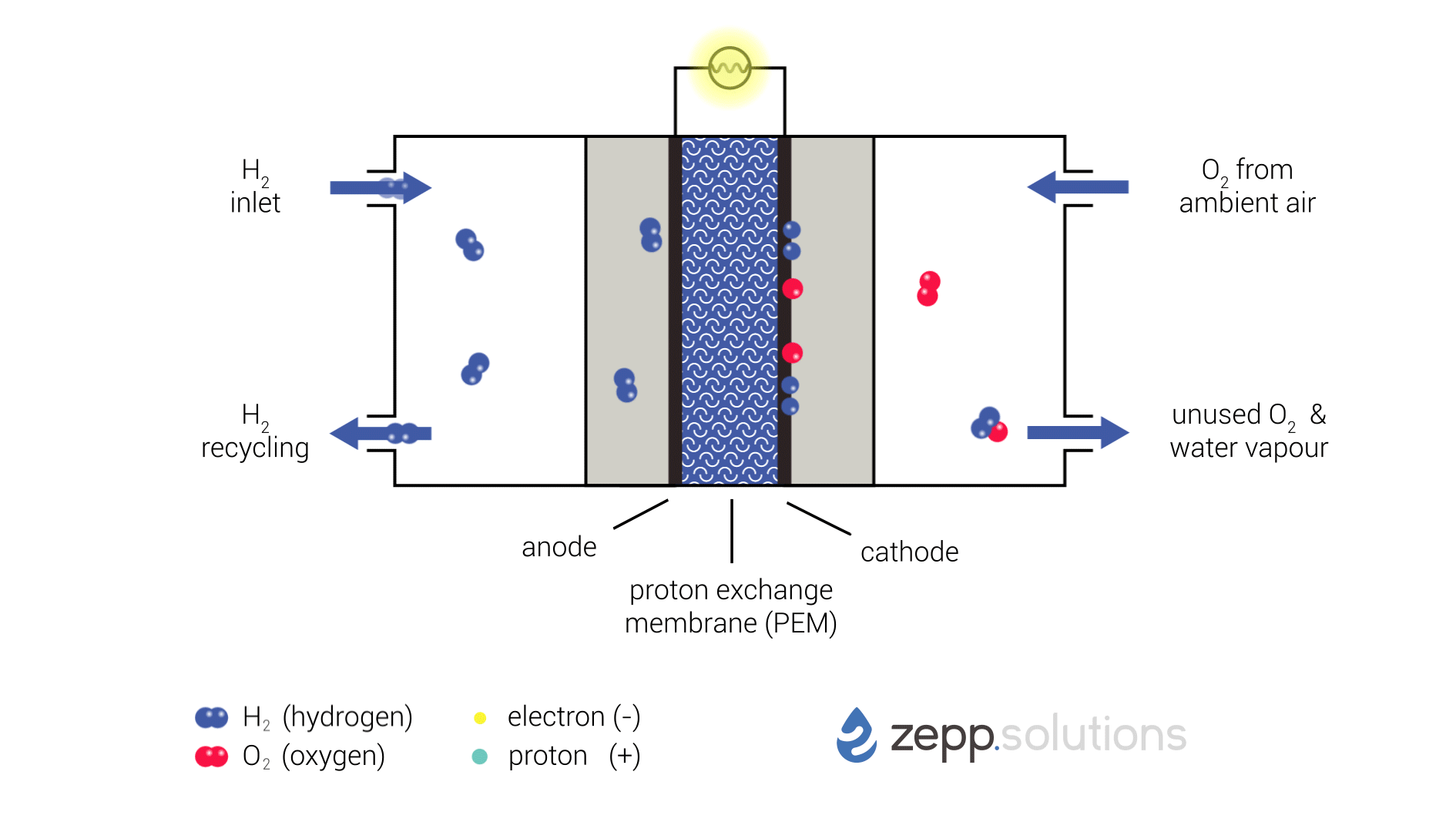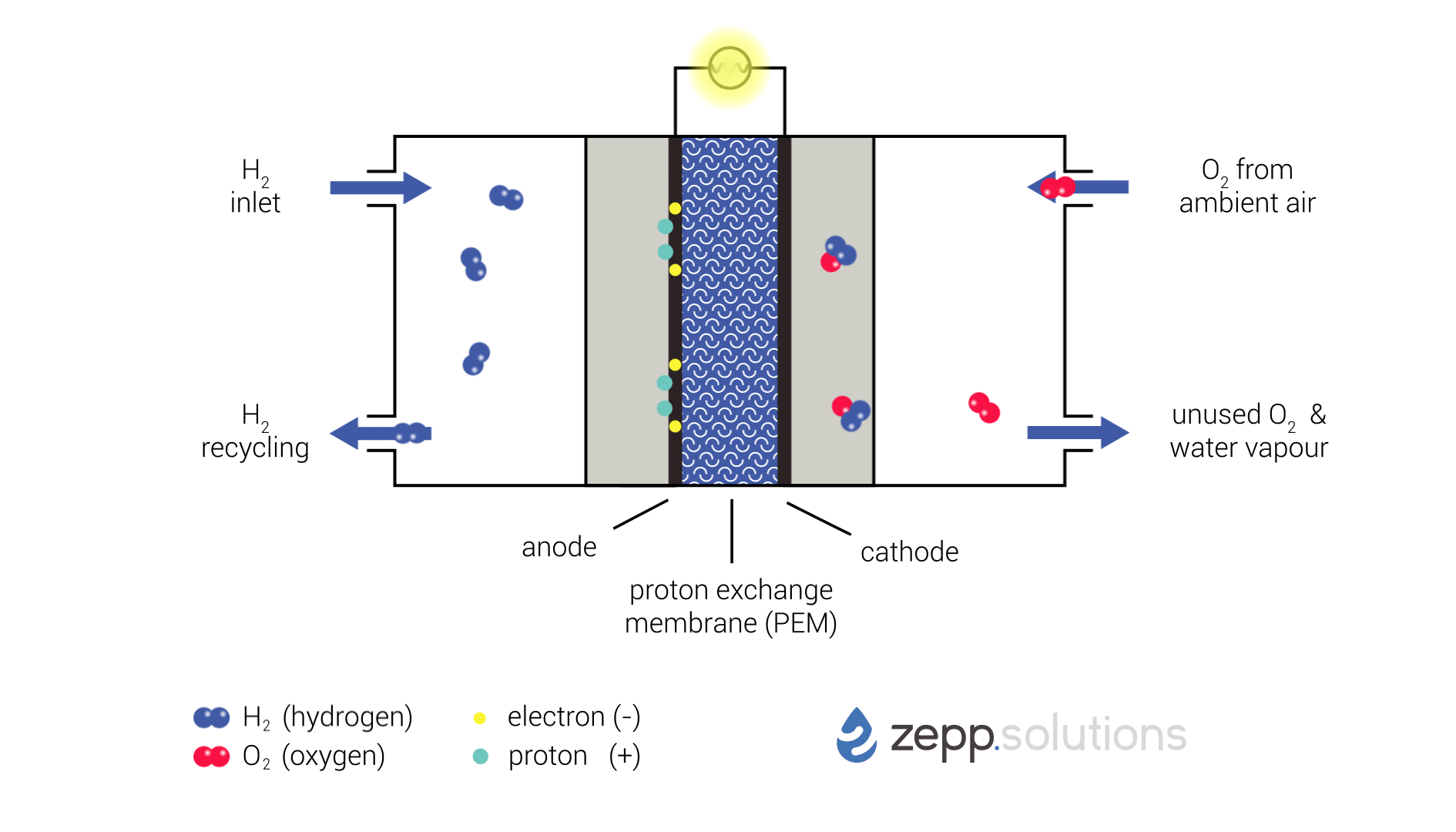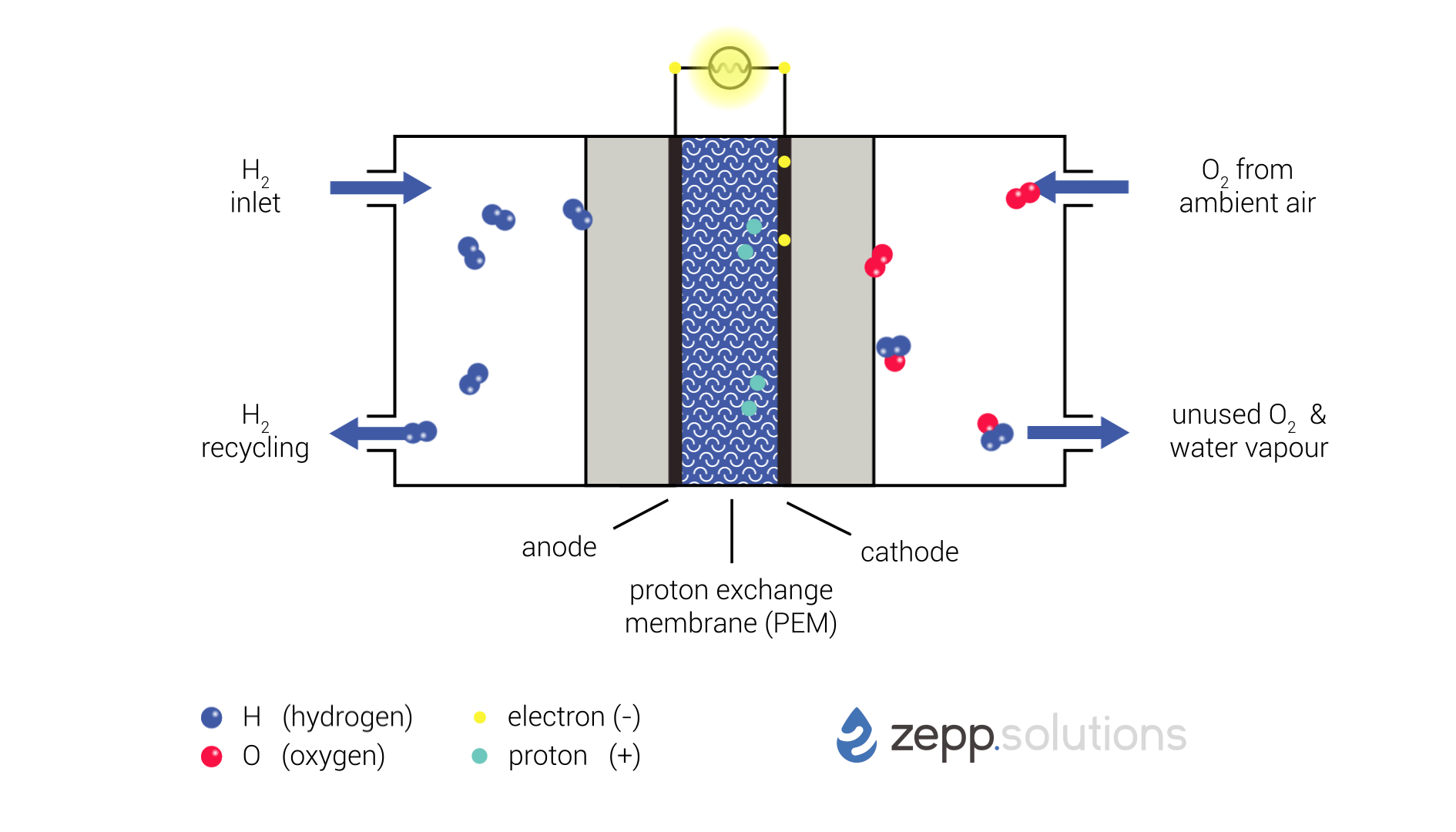
The infographic below shows this process in more detail. Hydrogen enters the fuel cell on the top left and splits into two protons and two electrons at the anode side. Hydrogen that doesn’t react is recirculated. The protons pass through the proton exchange membrane (PEM) in the middle, while the electrons take a detour. The electrons taking this detour provide the electrical energy used to power the application. On the right side of the PEM, at the cathode side, oxygen (O2) is split up and meets up with the protons and electrons. The protons and electrons together form hydrogen (H2), which bonds to the oxygen, resulting in water (H2O).
Hydrogen fuel cell technology is especially attractive for applications that combine a demand for high continuous power output with long operational uptimes. Current alternative energy storage systems, such as battery technology, require long charging times and the costs of these systems scale linearly with the required energy content. Twice the amount of energy requires twice the number of batteries, costing twice as much. For hydrogen-electric systems, only the amount of hydrogen storage has to be doubled, the fuel cell remains the same. Additionally, these operations benefit strongly from the quick refueling capabilities hydrogen fuel cell systems offer.
Fuel Cell Hybrid
To configure the optimum zero-emission power-system for our clients, we mostly deploy fuel cell hybrid systems, combining hydrogen fuel cell technology with a small battery energy storage. This battery energy storage acts as a buffer between the fuel cell and the powered application.
The results are uniquely designed fuel cell hybrid systems combining the best of both hydrogen and batteries, allowing for short refuelling times and long continuous operations at high energy demands, while being able to facilitate high peak loads without delay at a competitive overall system cost. The configuration, integration and operational control of these client-specific systems are our key competence.